Runs
Capture structured results from every test execution.
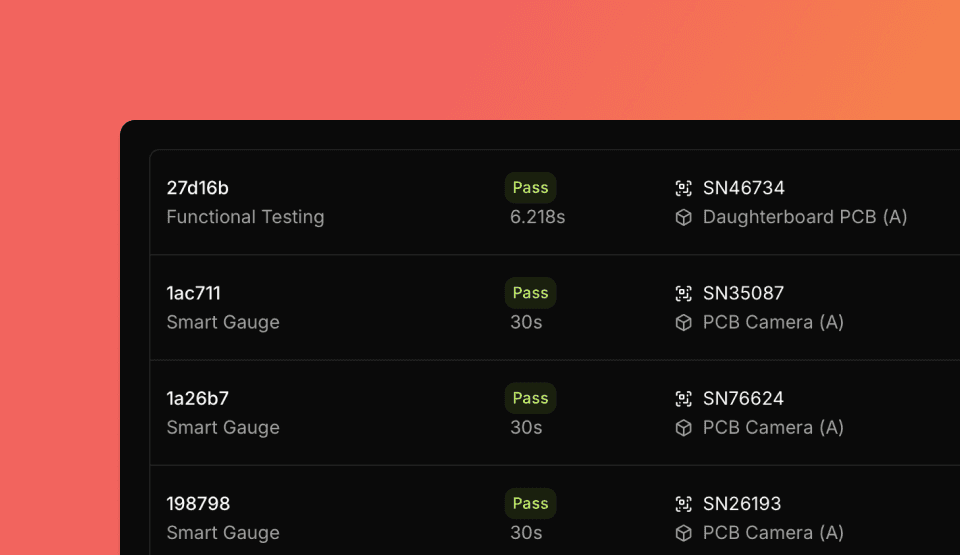
Overview
A Run captures everything from test execution: the unit being tested, procedure metadata, phases, measurements, logs, and attachments.
Create Runs
Create a procedure in TofuPilot and link it to your test script for automatic run generation.
Go to Procedures, click Create Procedure, and copy the
procedure_id (e.g., "FVT1").
Add the procedure_id to your test script to link execution to your
procedure.
Define the unit under test with serial_number and part_number.
Required Metadata
All runs require these fields:
- OpenHTF: Add
procedure_idandpart_numberto your Test, then provideserial_numberduring execution. TofuPilot automatically determines test outcome. - Python: Define
procedure_id,unit_under_test, andrun_passed.
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
procedure_id? | str | – |
serial_number? | str | – |
part_number? | str | – |
run_passed? | bool | – |
import openhtf as htf
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
def main():
test = htf.Test(
procedure_id="FVT1", # Link to the Procedure created in the app
part_number="PCB01", # Part number (required)
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001") # UUT serial number (required)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1", # Link to the Procedure created in the app (required)
unit_under_test={
"serial_number": "SN-0001", # Serial number (required)
"part_number": "PCB01" # Part number (required)
},
run_passed=True, # Boolean indicating if the run passed (required)
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Optional Metadata
Include additional metadata for better tracking:
- OpenHTF: Duration is calculated automatically from phase timestamps.
- Python: Set all metadata including duration manually.
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
procedure_version? | str | – |
duration? | timedelta | – |
batch_number? | str | – |
revision? | str | – |
import openhtf as htf
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
def main():
test = htf.Test(
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB01",
procedure_version="v2.1.0", # Track test procedure version
batch_number="2024-001",
revision="B",
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from datetime import timedelta
from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={
"serial_number": "SN-0001",
"part_number": "PCB01",
"batch_number": "2024-001",
"revision": "B",
},
procedure_version="v2.1.0", # Track test procedure version
duration=timedelta(minutes=2, seconds=34), # Manual duration for Python
run_passed=True,
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Phases
Phases organize tests into logical sections for easier debugging and analysis.
- OpenHTF: Define phase functions in your script. TofuPilot captures name, outcome, and timing automatically.
- Python: Create phase dictionaries with timing, outcome, and measurements.
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
name? | str | – |
outcome? | "PASS" | "FAIL" | "ERROR" | "SKIP" | – |
start_time_millis? | number | – |
end_time_millis? | number | – |
measurements? | array | – |
import openhtf as htf
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
def phase_one(test): # Phase name is taken from the function name
return htf.PhaseResult.CONTINUE # Pass outcome
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_one,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB1"
)
with TofuPilot(test):
# Duration and start time are set automatically
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from tofupilot import PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
client = TofuPilotClient()
def phase*one():
start_time_millis = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
phase = {
"name": "phase*one",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start_time_millis,
"end_time_millis": start_time_millis + 30 * 1000, # 30 seconds
}
return phase
def main():
phases = [phase_one()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Measurements
Measurements capture test data like voltage, temperature, or pass/fail conditions. Support includes simple values and multi-dimensional arrays.
- OpenHTF: Use measurement decorators to define values, ranges, and units. TofuPilot handles collection and validation automatically.
- Python: Build measurement dictionaries with values, units, validators, and outcomes.
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
name? | string | – |
measured_value? | number | string | boolean | dict | – |
outcome? | "PASS" | "FAIL" | "UNSET" | – |
units? | string | – |
validators? | array | – |
aggregations? | array | – |
import openhtf as htf
from openhtf.util import units
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
# Decorator to set measurement name, unit and limits
@htf.measures(htf.Measurement("voltage").in_range(3.1,
3.5).with_units(units.VOLT))
# Phase returns a Pass status because measurement (3.3) passes all validators
def phase_voltage_measure(test):
test.measurements.voltage = 3.3
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_voltage_measure,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB1")
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
client = TofuPilotClient()
# Phase returns a Pass status because measurement (3.3) passes all validators
def phase_voltage_measure():
start_time_millis = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
phase = {
"name": "voltage_measure_phase",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start_time_millis,
"end_time_millis": start_time_millis
+ 30 * 1000, # Indicating phase took 30 seconds to complete
"measurements": [
{
"name": "voltage",
"units": "V",
"measured_value": 3.3,
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"validators": [
{"operator": ">=", "expected_value": 3.1, "outcome": "PASS"},
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 3.5, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
}
],
}
return phase
def main():
phases = [phase_voltage_measure()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1", # Create the procedure first in the Application
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(
phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()
Numerical
Record numeric values like voltage, resistance, or temperature:
import openhtf as htf
from openhtf.util import units
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
@htf.measures(
htf.Measurement("temperature") # Declares the measurement name
.in_range(0, 100) # Defines the lower and upper limits
.with_units(units.DEGREE_CELSIUS) # Specifies the unit
)
def phase_temp(test): # Record numerical measurement - temperature value
test.measurements.temperature = 25.3
return htf.PhaseResult.CONTINUE
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_temp,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB1"
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from datetime import datetime
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
def phase_temperature():
start_time_millis = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
return {
"name": "phase_temperature",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start_time_millis,
"end_time_millis": start_time_millis + 1000,
"measurements": [
{
"name": "temperature",
"measured_value": 25.3, # Numerical measurement - temperature value
"units": "C",
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"validators": [
{"operator": ">=", "expected_value": 0, "outcome": "PASS"},
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 100, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
}
],
}
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
phases = [phase_temperature()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()String
Record text values like serial numbers, firmware versions, or responses:
import openhtf as htf
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
@htf.measures(htf.Measurement("firmware_version").equals("1.2.4"))
def phase_firmware(test): # Record string measurement - firmware version
test.measurements.firmware_version = "1.2.4"
return htf.PhaseResult.CONTINUE
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_firmware,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB1"
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from datetime import datetime
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
def phase_firmware():
start_time_millis = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
return {
"name": "phase_firmware",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start_time_millis,
"end_time_millis": start_time_millis + 1000,
"measurements": [
{
"name": "firmware_version",
"measured_value": "1.2.4", # String measurement - firmware version
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"validators": [
{"operator": "==", "expected_value": "1.2.4", "outcome": "PASS"},
],
}
],
}
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
phases = [phase_firmware()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Boolean
Record true/false values for conditions, flags, or states:
import openhtf as htf
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
@htf.measures(htf.Measurement("is_led_switch_on").equals(True))
def phase_led(test): # Record boolean measurement - LED switch state
test.measurements.is_led_switch_on = True
return htf.PhaseResult.CONTINUE
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_led,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB1"
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from datetime import datetime
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
def phase_led():
start_time_millis = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
return {
"name": "phase_led",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start_time_millis,
"end_time_millis": start_time_millis + 1000,
"measurements": [
{
"name": "is_led_switch_on",
"measured_value": True, # Boolean measurement - LED switch state
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"validators": [
{"operator": "==", "expected_value": True, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
}
],
}
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
phases = [phase_led()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Multi-dimensional
Record time-series data with multiple dimensions. The Python client supports validators and aggregations at two levels:
- Measurement level: applies to the entire measurement
- Data series level: applies to a specific axis
Data series object:
Python client only. OpenHTF supports multi-dimensional data via
.with_dimensions() but not validators or aggregations.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
data | array | Array of numeric data points |
units | string | Unit for this axis |
validators | array | Validator objects for this axis |
aggregations | array | Aggregation objects computed over this axis data |
import random
import openhtf as htf
from openhtf.util import units
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
@htf.measures(
htf.Measurement("current_voltage_resistance_over_time")
.with_dimensions(
units.SECOND, units.VOLT, units.AMPERE
) # Input axes: time, voltage, current
.with_units(units.OHM) # Output unit: resistance in ohms
)
def power_phase(test): # Record multi-dimensional measurement - time series data
for t in range(100):
timestamp = t / 100
voltage = round(random.uniform(3.3, 3.5), 2)
current = round(random.uniform(0.3, 0.8), 3)
resistance = voltage / current
test.measurements.current_voltage_resistance_over_time[
timestamp, voltage, current
] = resistance
return htf.PhaseResult.CONTINUE
def main():
test = htf.Test(
power_phase,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB1"
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from datetime import datetime
import numpy as np
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
def numpy_way():
"""NumPy approach with validators and aggregations"""
start = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
# Generate data for multi-dimensional measurement
timestamps = np.linspace(0, 0.4, 5).tolist()
voltages = [3.3, 3.35, 3.32, 3.28, 3.31]
return {
"name": "vector_approach",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start,
"end_time_millis": start + 30000,
"measurements": [
{
"name": "voltage_over_time",
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
# Measurement-level validators/aggregations
"validators": [
{"operator": "==", "expected_value": True, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
"aggregations": [
{"type": "point_count", "value": 5, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
# Per-axis data with validators/aggregations
"data_series": [
{
"data": timestamps,
"units": "s",
},
{
"data": voltages,
"units": "V",
"validators": [
{"operator": ">=", "expected_value": 3.0, "outcome": "PASS"},
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 3.6, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
"aggregations": [
{
"type": "mean",
"value": 3.31,
"outcome": "PASS",
"validators": [
{"operator": ">=", "expected_value": 3.2, "outcome": "PASS"},
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 3.4, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
},
],
},
],
}
],
}
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
phases = [numpy_way()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Click the Chart icon in Run > Phases to visualize multi-dimensional data.
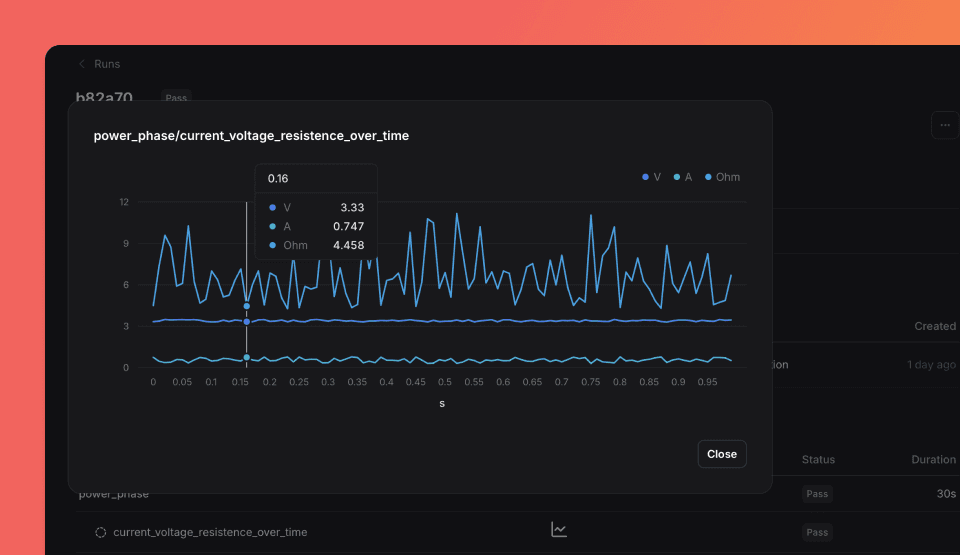
Validators
Validators define validation rules for measurements. Each validator specifies an operator, expected value, and outcome.
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
operator? | "≥" | "≤" | ">" | "<" | "==" | "!=" | "in" | "not in" | "matches" | – |
expected_value? | number | string | boolean | array | – |
outcome? | "PASS" | "FAIL" | "UNSET" | UNSET |
is_decisive? | boolean | true |
expression? | string | – |
from datetime import datetime
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
def phase_voltage_with_validators():
start_time_millis = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
return {
"name": "phase_voltage",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start_time_millis,
"end_time_millis": start_time_millis + 1000,
"measurements": [
{
"name": "voltage",
"units": "V",
"measured_value": 3.3,
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"validators": [
{"operator": ">=", "expected_value": 3.1, "outcome": "PASS"},
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 3.6, "outcome": "FAIL", "is_decisive": False}, # Warning only
],
}
],
}
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
phases = [phase_voltage_with_validators()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Type matching rules:
The expected_value type must match the measurement's measured_value type:
| Measurement type | Valid expected_value types | Valid operators |
|---|---|---|
number | number, array[number] | >=, <=, >, <, ==, !=, in, not in |
string | string, array[string] | ==, !=, in, not in, matches |
boolean | boolean | ==, != |
On type mismatch: If expected_value type doesn't match measurement type, the validator is stored as expression-only (structured fields cleared, data preserved in expression).
Expression usage:
The expression field serves two purposes:
- Custom display: Provide human-readable text for complex validations
- Fallback storage: On type mismatch, structured data is converted to expression
Some analytics features require structured validators with operator and
expected_value. Expression-only validators are for display purposes and
won't be included in these analytics.
Aggregations
Attach computed results (statistics, derived values) to measurements with optional validation.
Aggregations are only available with the Python client. OpenHTF does not support aggregations natively.
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
type | string | – |
value? | number | string | boolean | – |
unit? | string | – |
outcome? | "PASS" | "FAIL" | "UNSET" | UNSET |
validators? | array | – |
from datetime import datetime
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
def phase_temperature_stability():
start = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
temperatures = [25.1, 25.3, 25.2, 25.4, 25.3] # Sampled over time
return {
"name": "temperature_stability",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start,
"end_time_millis": start + 60000,
"measurements": [
{
"name": "temperature",
"units": "°C",
"measured_value": temperatures,
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"aggregations": [
{
"type": "mean",
"value": 25.26,
"outcome": "PASS",
"validators": [
{"operator": ">=", "expected_value": 20, "outcome": "PASS"},
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 30, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
},
{
"type": "std",
"value": 0.11,
"outcome": "PASS",
"validators": [
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 1.0, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
},
],
}
],
}
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
phases = [phase_temperature_stability()]
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "PCB1A001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(phase["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for phase in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Multiple Measurements
Record multiple measurements within one phase:
import random
import openhtf as htf
from openhtf.util import units
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
@htf.measures(
htf.Measurement("is_connected").equals(True), # Boolean measure
htf.Measurement("firmware_version").equals("1.2.7"), # String measure
htf.Measurement("input_voltage").in_range(3.2, 3.4).with_units(units.VOLT),
htf.Measurement("input_current").in_range(
maximum=1.5).with_units(units.AMPERE),
)
def phase_multi_measurements(test):
test.measurements.is_connected = True
test.measurements.firmware_version = "1.2.7"
test.measurements.input_voltage = round(random.uniform(3.29, 3.42), 2)
test.measurements.input_current = round(random.uniform(1.0, 1.55), 3)
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_multi_measurements,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB01",
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "PCB1A004")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()import random
from datetime import datetime
from tofupilot import MeasurementOutcome, PhaseOutcome, TofuPilotClient
client = TofuPilotClient()
def phase_multi_measurements():
start_time_millis = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
is_connected = True
firmware_version = "1.2.7"
input_voltage = round(random.uniform(3.29, 3.42), 2)
input_current = round(random.uniform(1.0, 1.55), 3)
phase = [
{
"name": "phase_multi_measurements",
"outcome": PhaseOutcome.PASS,
"start_time_millis": start_time_millis,
"end_time_millis": start_time_millis + 5000,
"measurements": [
{
"name": "is_connected",
"measured_value": is_connected,
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"validators": [
{"operator": "==", "expected_value": True, "outcome": "PASS"},
],
},
{
"name": "firmware_version",
"measured_value": firmware_version,
"outcome": MeasurementOutcome.PASS,
"validators": [
{"operator": "==", "expected_value": "1.2.7", "outcome": "PASS"},
],
},
{
"name": "input_voltage",
"units": "V",
"measured_value": input_voltage,
"outcome": (
MeasurementOutcome.PASS
if 3.2 <= input_voltage <= 3.4
else MeasurementOutcome.FAIL
),
"validators": [
{"operator": ">=", "expected_value": 3.2, "outcome": "PASS" if input_voltage >= 3.2 else "FAIL"},
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 3.4, "outcome": "PASS" if input_voltage <= 3.4 else "FAIL"},
],
},
{
"name": "input_current",
"units": "A",
"measured_value": input_current,
"outcome": (
MeasurementOutcome.PASS
if input_current <= 1.5
else MeasurementOutcome.FAIL
),
"validators": [
{"operator": "<=", "expected_value": 1.5, "outcome": "PASS" if input_current <= 1.5 else "FAIL"},
],
},
],
}
]
return phase
def main():
phases = phase_multi_measurements()
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={
"serial_number": "PCB1A004",
"part_number": "PCB01",
},
phases=phases,
run_passed=all(p["outcome"] == PhaseOutcome.PASS for p in phases),
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()View detailed results on the run page after test completion.
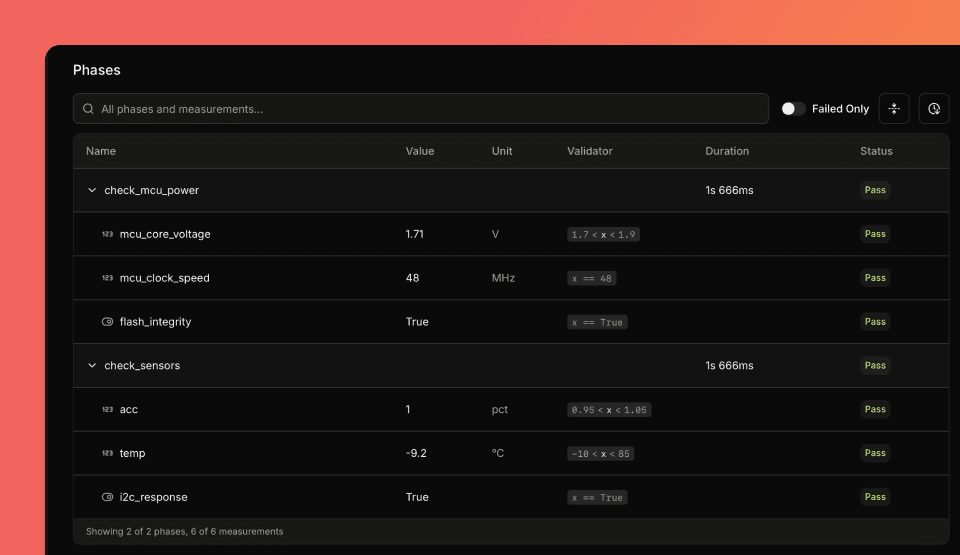
Attachments
Attach files like screenshots, CSV data, or diagnostic images alongside test results.
- OpenHTF: Use
attachorattach_from_filefunctions to include files. - Python: Pass file paths in the
attachmentsparameter.
import openhtf as htf
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
def phase_file_attachment(test):
test.attach_from_file("data/temperature-map.png") # Replace with your file path
return htf.PhaseResult.CONTINUE
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_file_attachment,
procedure_id="FVT1", # Create the procedure first in the Application
part_number="PCB01",
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
def phase_file_attachment():
file_paths = ["data/temperature-map.png"] # Replace with your file paths
return file_paths
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
attachments = phase_file_attachment()
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1", # Create the procedure first in the Application
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "SN-0001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
run_passed=True,
attachments=attachments,
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()By default, the JSON report generated by OpenHTF is included as an attachment.
Logs
Logs help debug test execution and unusual behavior.
- OpenHTF: Use the OpenHTF logger from any phase. TofuPilot captures all log levels and makes them searchable.
- Python: Create your own logging handler to capture messages.
import openhtf as htf
from tofupilot.openhtf import TofuPilot
@htf.measures(htf.Measurement("boolean_measure").equals(True))
def phase_with_info_logger(test):
test.measurements.boolean_measure = True # You can log info, warning, error, and critical. By default, debug.
test.logger.info("Logging an information")
def main():
test = htf.Test(
phase_with_info_logger,
procedure_id="FVT1",
part_number="PCB01",
)
with TofuPilot(test):
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()import logging
import sys
from datetime import datetime
from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
class TofuPilotLogHandler(logging.Handler):
"""Handler that captures logs in a format compatible with TofuPilot API."""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.logs = []
def emit(self, record):
# Format log with ISO-8601 timestamp (UTC, ms) for TofuPilot API
log_entry = {
"level": record.levelname,
"timestamp": datetime.utcfromtimestamp(record.created).isoformat(
timespec="milliseconds"
) + "Z",
"message": record.getMessage(),
"source_file": record.filename,
"line_number": record.lineno,
}
self.log.append(log_entry)
# Initialize the TofuPilot client to report test results
client = TofuPilotClient()
# Set up local logger with custom name and prevent propagation to parent loggers
local_logger = logging.getLogger("test_logger")
local_logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
local_logger.propagate = False
# Add handlers: one for TofuPilot API capture and one for console output
capture_handler = TofuPilotLogHandler()
local_logger.addHandler(capture_handler)
local_logger.addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout))
# Log examples at different severity levels
local_logger.debug("Debug message: Detailed information for troubleshooting")
local_logger.info("Info message: Normal operation information")
local_logger.warning("Warning: Something unexpected but not critical")
local_logger.error("Error: A significant problem that needs attention")
local_logger.critical("Critical: System unstable, immediate action required")
# Create a run and send captured logs to TofuPilot
try:
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": "SN-0001", "part_number": "PCB01"},
run_passed=True,
logs=capture_handler.logs,
)
finally:
local_logger.removeHandler(capture_handler)Get Runs
Retrieve runs programmatically for analysis or integration. Most commonly by serial number.
from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
from pathlib import Path
import json
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
serial_number = "SN-0001"
# Create a run
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": serial_number, "part_number": "PCB01"},
run_passed=True,
)
# Get the run(s) for this serial number "SN-0001"
res = client.get_runs(serial_number=serial_number)
# Save the response data to a JSON file
output_file = Path(__file__).parent / f"run_data_{serial_number}.json"
with open(output_file, "w") as f:
json.dump(res, f, indent=2)
print(f"Run data saved to: {output_file}")
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Get Attachments
The get_runs() function also retrieves attachments as downloadable URLs. This enables programmatic access to files uploaded during test execution.
from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
import requests
from pathlib import Path
def main(): # Initialize client and create a test run with attachment
client = TofuPilotClient()
serial_number = "SN-0001"
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1",
unit_under_test={"serial_number": serial_number, "part_number": "PCB01"},
run_passed=True,
attachments=["data/temperature-map.png"], # Update with your file path
)
# Then fetch the created run using the serial number
res = client.get_runs(serial_number=serial_number)
# Download and save each attachment next to the script
attachments = res["data"][0]["attachments"]
for attachment in attachments:
response = requests.get(attachment["url"])
response.raise_for_status()
file_path = Path(__file__).parent / attachment["name"]
with open(file_path, "wb+") as f:
f.write(response.content)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()Upload Runs offline
Run tests offline and upload results when connectivity is available.
- OpenHTF: Save results as JSON files, then use
create_run_from_openhtf_report()to upload. See OpenHTF output callbacks documentation. - Python: Use
create_run()withstarted_atto preserve test time. Without it, upload time is used.
from openhtf import PhaseResult, Test
from openhtf.output.callbacks import json_factory
from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
def power_on_test(test):
return PhaseResult.CONTINUE
# Run test and save results to JSON
def execute_test(file_path):
test = Test(
power_on_test,
part_number="PCB01",
procedure_id="FVT1"
) # Save results as JSON
test.add_output_callbacks(json_factory.OutputToJSON(file_path, indent=2))
test.execute(lambda: "SN-0001")
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
# Test results file path
file_path = "./test_result.json"
execute_test(file_path)
# Upload results to TofuPilot
client.create_run_from_openhtf_report(file_path)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from tofupilot import TofuPilotClient
def main():
client = TofuPilotClient()
client.create_run(
procedure_id="FVT1", # Create the procedure first in the Application
started_at=datetime.now() - timedelta(days=1), # Run performed the day before
unit_under_test={
"serial_number": "SN-0001",
"part_number": "PCB01",
},
run_passed=True,
)
if **name** == "**main**":
main()How is this guide?